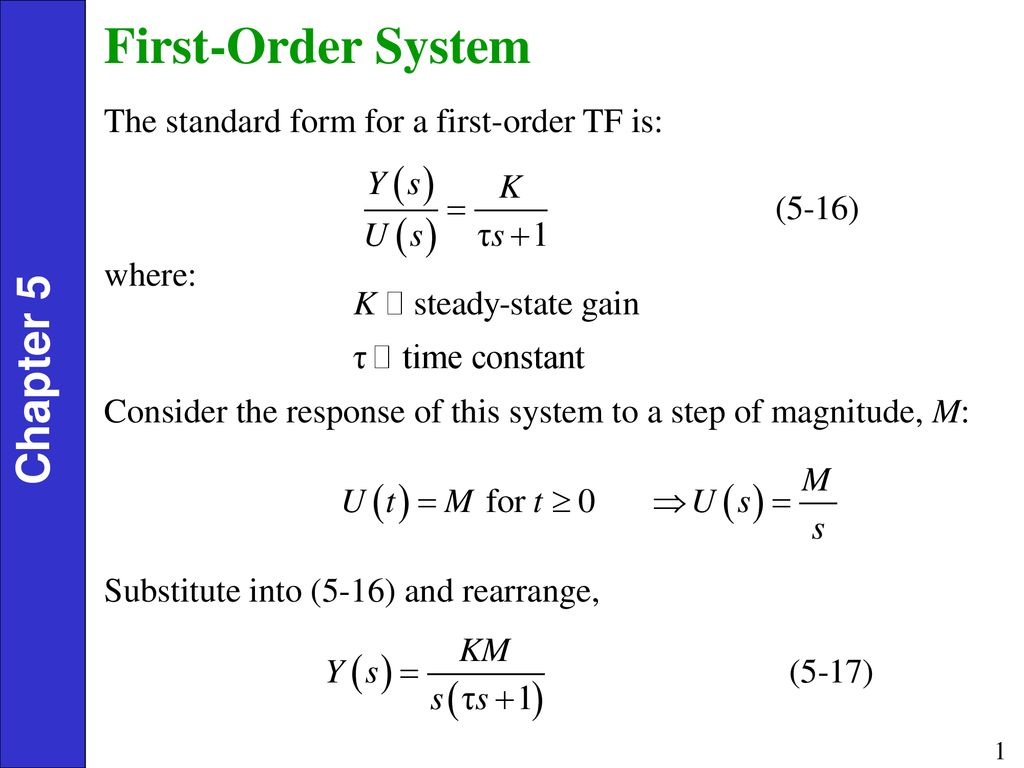
First Order System Definition
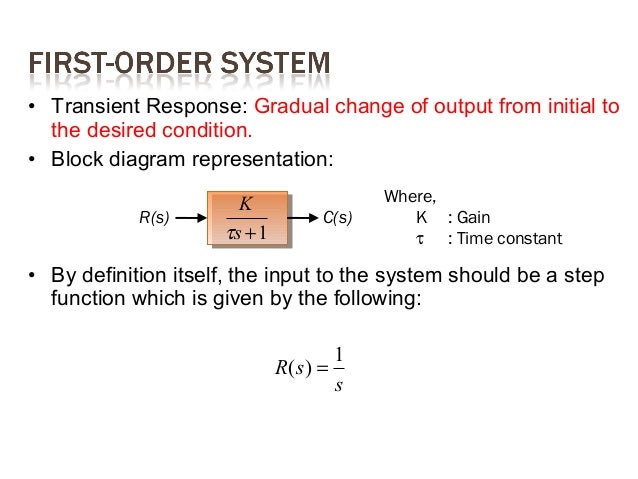
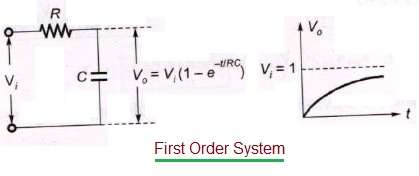
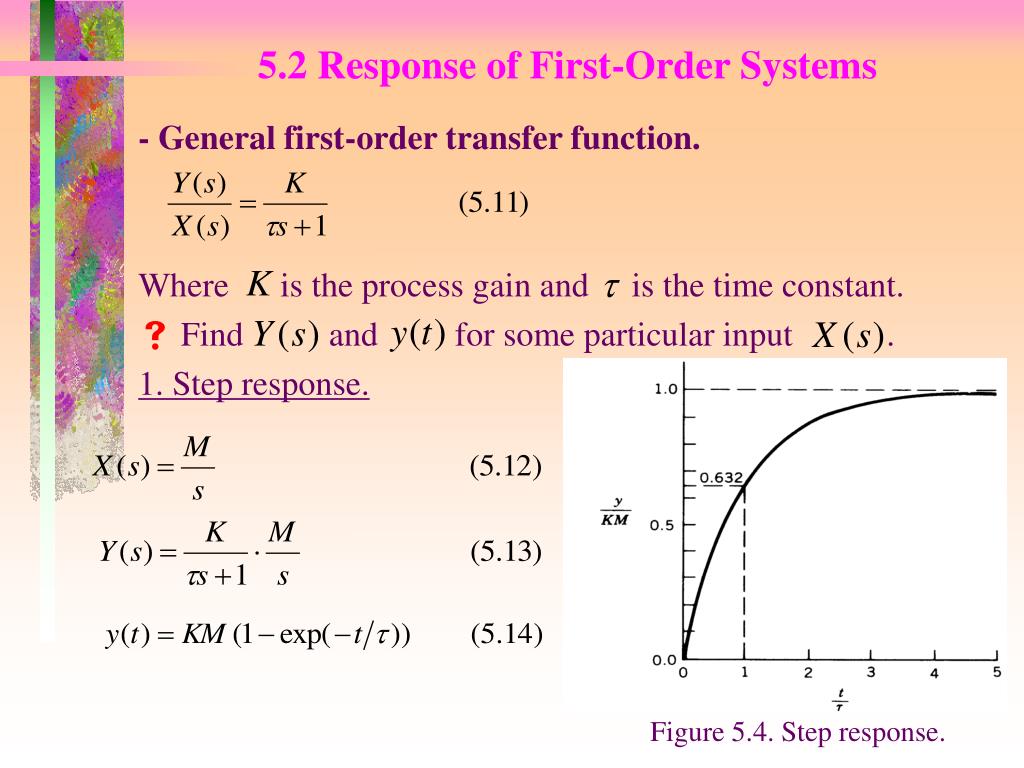
First order system definition. Step Response of a first order system. Where T is known as time constant of the system and it is defined as the time required for the signal to attain 632 of final or steady state value. Taking the inverse Laplace of above equation is.
In this equation if 𝑎1 0 it is no longer an differential equation and so 𝑎1 cannot be 0. They have many forms. Response of 1 st order system when the input is unit step - For Unit Step Now the partial fraction of above equation will be.
A solution of the first-order difference equation xt f t xt1 is a function x of a single variable whose domain is the set of integers such that xt f t xt1 for every integer t where xt denotes the value of x at t. When studying differential equations we denote the value at t of a solution x by x t. The behavior of the systems are qualitatively similar.
A second-order intentional system is more sophisticated. All exhibit a non-oscillating decay to the equilibrium state Vc 0 or q 0. The simple first-order political discriminator experiences no conflict in categorizing disvaluees as inferior beings to be suppressed and exploited.
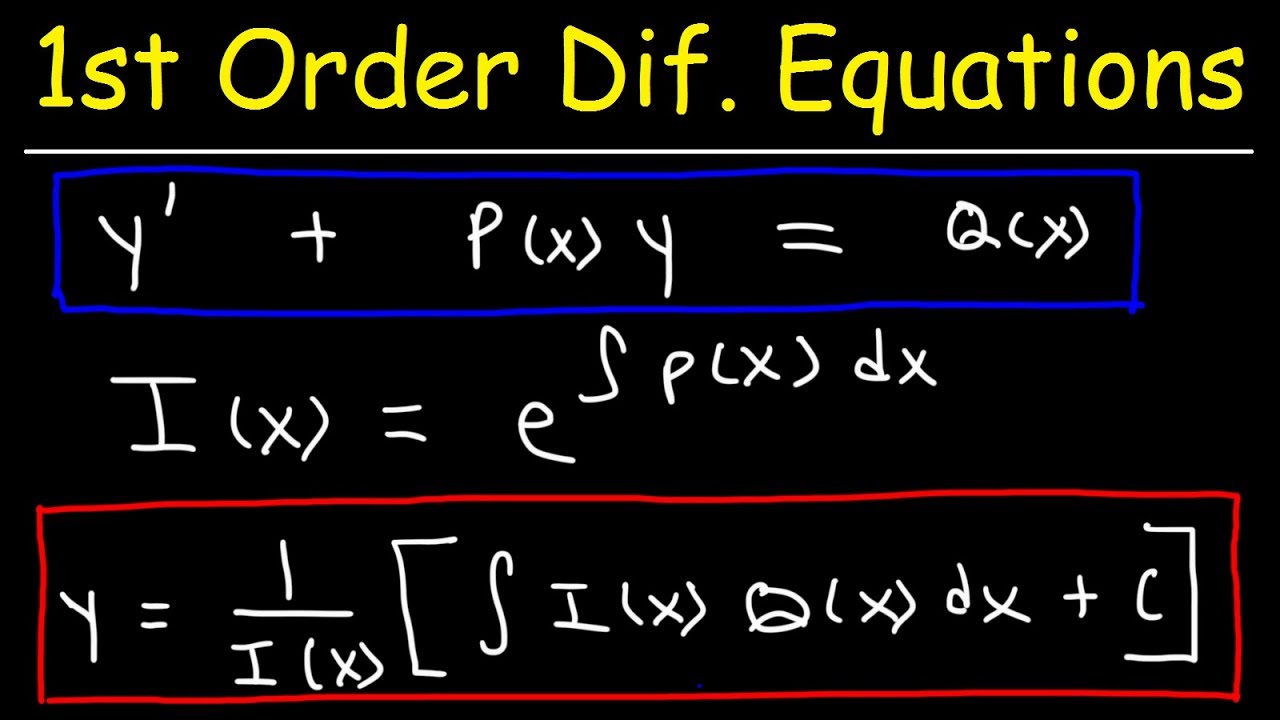
First Order is short for First-Order Ordinary Differential Equation And the same goes for Second order. Where a b and c are constants. The definition of an Ordinary Differential Equation is an equation containing a function of one independent variable and its derivatives.
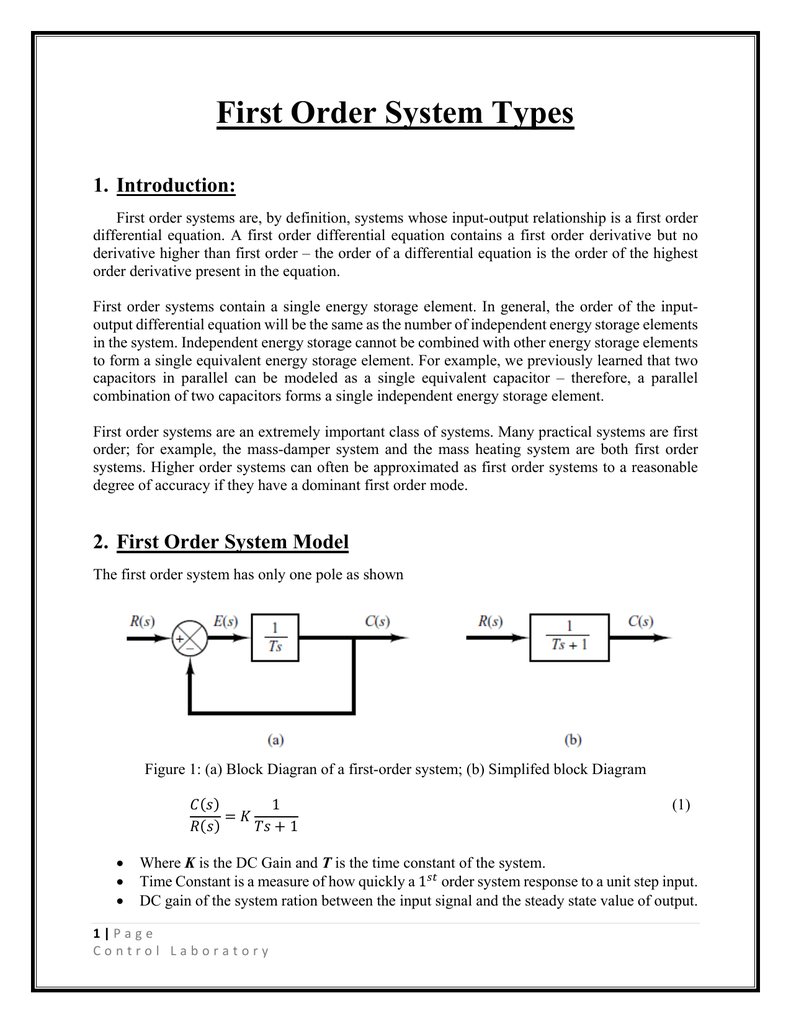
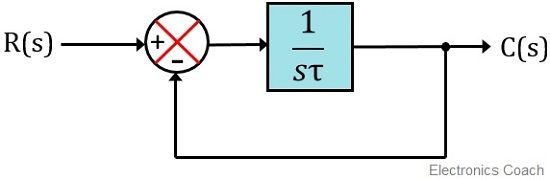
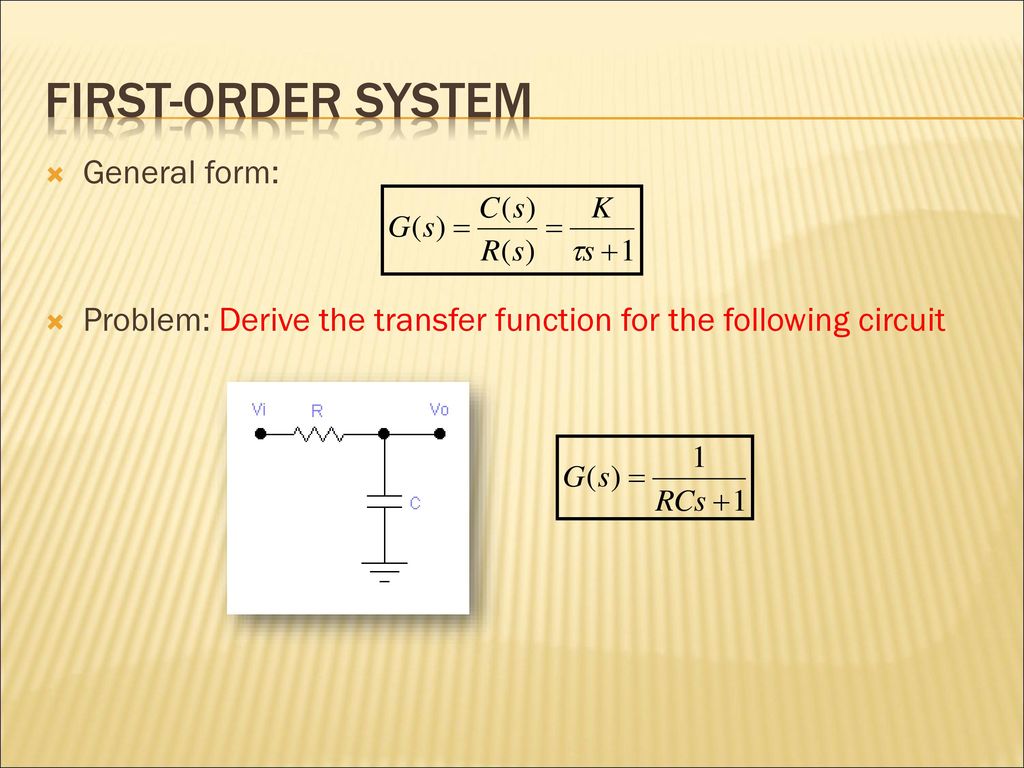
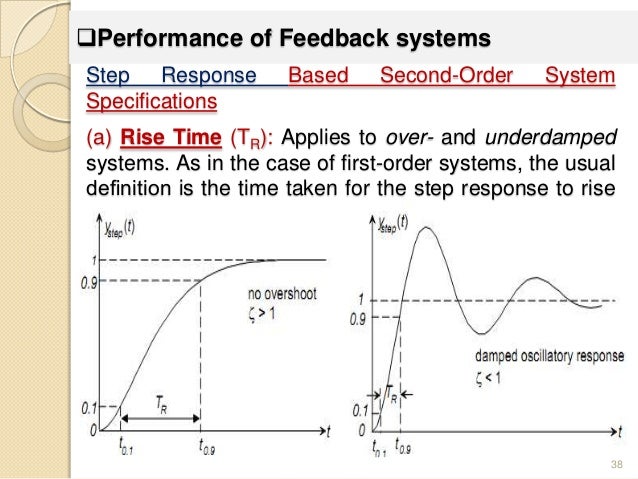
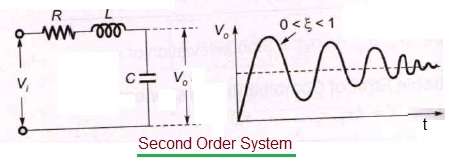
First order systems are by definition systems whose input-output relationship is a first order differential equation. The order of a differential equation is determined by the power of the differential aka if you are doing a derivative once or twice. Second Order Systems - 3 The static sensitivity K S should really be called the pseudo-static sensitivityIt is determined as the response of the measurement system if it had no mass and no damping ie the response of the equivalent zero-th order system.
The forcing function of the ODE The equation is often rearranged to the form Tau is. 1 Relating to the simplest or most fundamental level of organization experience or analysis.
The system response to an initial condition y0 is.
The order of a differential equation is determined by the power of the differential aka if you are doing a derivative once or twice. So the step signal is widely used in the time domain for analyzing the control systems from their responses. Taking the inverse Laplace of above equation is. A solution of the first-order difference equation xt f t xt1 is a function x of a single variable whose domain is the set of integers such that xt f t xt1 for every integer t where xt denotes the value of x at t. When studying differential equations we denote the value at t of a solution x by x t. Where T is known as time constant of the system and it is defined as the time required for the signal to attain 632 of final or steady state value. 1 0 10 which has a single root 1. Time behavior of a system is important. An Initial Value Problem is a system of first order ordinary differential equations with initial conditions where.
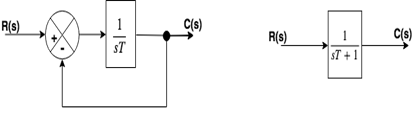
The system response to an initial condition y0 is. The relationship between the output and the input is given by the following equation. First-order predicate a predicate that takes only individual s constants or variables as argument s First-order predicate calculus. When talking about dynamic systems the order is defined on the maximum order of the differential equations which describes the dynamics system. Second Order Systems - 3 The static sensitivity K S should really be called the pseudo-static sensitivityIt is determined as the response of the measurement system if it had no mass and no damping ie the response of the equivalent zero-th order system. It is a system whose dynamic behavior is described by a first order differential equation. They have many forms.













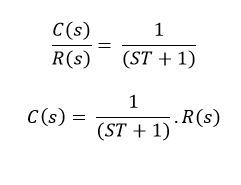















Post a Comment for "First Order System Definition"